Power of Power Integrity Analysis in High-Speed Digital Designs
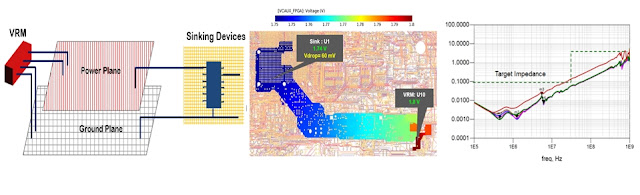
The Emergence of Power Integrity Analysis As the speed of the data signal increases, many reasons including power supply noise lead to the degradation of the high-speed signals. In low power high-speed digital interfaces, it is crucial to characterize the whole system power supply in order to minimize power supply noise in the system. High-speed design failures show up as failures at higher operating frequency, data error rates, cross talk errors, and EMI errors. Currently, PI engineers do PI analysis of power system to ensure proper and reliable operation using Electronic Design Automation tools (EDA) before the actual fabrication of board. This reduces board failure chances significantly and also cuts production time. SI and PI are two distinct but related realms of analysis concerned with the proper operation of digital circuits. In SI, the main concern is to make sure that transmitted 1s looks like 1s at the receiver (and same for the 0s). In PI, the main...

